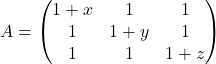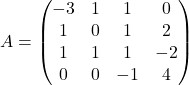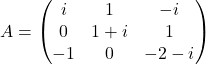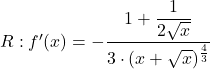23 Naloge brez postopka reševanja
Naloga 1: Naj bosta dani matriki 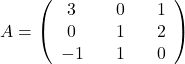 in
in 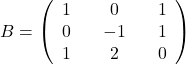 .
.
Rešite matrično enačbo ![]() .
.
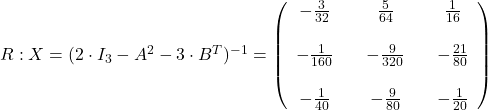
Naloga 2: Izračunajte vrednost determinante matrike ![]() .
.
Naloga 3: Rešite sistem linearnih enačb.
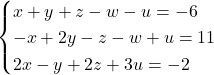
![]() .
.
Naloga 4: Rešite sistem linearnih enačb.
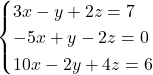
![]() : Sistem ni rešljiv.
: Sistem ni rešljiv.
Naloga 5: Rešite sistem linearnih enačb.
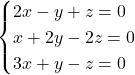
![]() .
.
Naloga 6: Rešite sistem linearnih enačb.
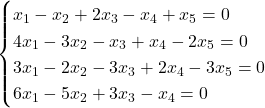
![]() .
.
Naloga 7: Poiščite lastne vrednosti in lastne vektorje matrike ![]() ter algebraične in geometrične večkratnosti njenih lastnih vrednosti.
ter algebraične in geometrične večkratnosti njenih lastnih vrednosti.
-
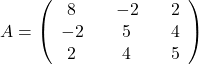
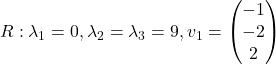 ,
, 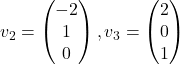
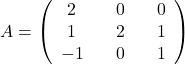
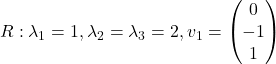 ,
, 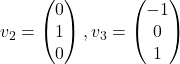
-
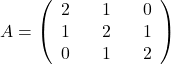
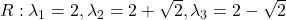 ,
, 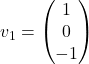
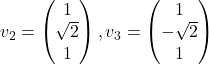
-

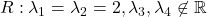 ,
, 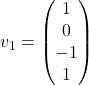
-
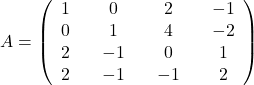
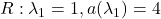 ,
, 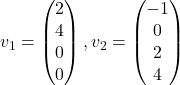 ,
, 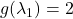
Naloga 8: Zapišite enačbo ravnine ![]() , ki vsebuje točko
, ki vsebuje točko ![]() in je vzporedna premicama
in je vzporedna premicama ![]() in
in ![]() .
.
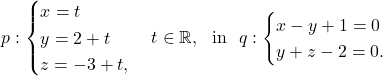
![]() : Enačba ravnine
: Enačba ravnine ![]() .
.
Naloga 9: Poiščite enačbo premice ![]() , ki leži v ravnini
, ki leži v ravnini ![]() in ki pod pravim kotom seka premico
in ki pod pravim kotom seka premico ![]() , podano s presekom ravnin
, podano s presekom ravnin ![]() ter
ter ![]() .
.
![]() :
: 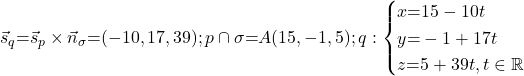
Naloga 10: Izračunajte naslednje limite:
Naloga 11: Poiščite konstanti ![]() in
in ![]() tako, da velja
tako, da velja
![]()
![]()
Naloga 12: Poiščite konstanti ![]() in
in ![]() tako, da velja
tako, da velja
![]()
![]()
Naloga 13: Določite, če obstajajo, asimptote naslednjih funkcij:
Naloga 14: Naj bo funkcija ![]() podana s predpisom
podana s predpisom ![]() , kjer je
, kjer je ![]() ter
ter ![]() domena funkcije
domena funkcije ![]() .
.
- Določite vrednost parametra
 tako, da je premica
tako, da je premica  navpična asimptota dane funkcije.
navpična asimptota dane funkcije.
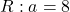
- Določite domeno funkcije
 ter vse njene asimptote.
ter vse njene asimptote.
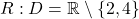
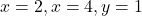
Naloga 15: Naj bo funkcija ![]() podana s predpisom
podana s predpisom ![]() . Določite vrednost parametra
. Določite vrednost parametra ![]() tako, da je premica
tako, da je premica ![]() poševna asimptota dane funkcije.
poševna asimptota dane funkcije.
![]()
Naloga 16: Določite vrednost parametra ![]() tako, da je funkcija
tako, da je funkcija ![]() , podana s predpisom
, podana s predpisom 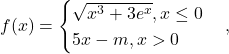 zvezna pri točki
zvezna pri točki ![]() .
.
![]()
Naloga 17: Določite vrednost realnega parametra ![]() tako, da je funkcija
tako, da je funkcija ![]() , podana s predpisom
, podana s predpisom ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com f(x)=\begin{cases} a, \ \ \mbox{če je} \ \ x\leq 0 \\ \displaystyle\frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt[3]{x}-1},\ \ \mbox{če je} \ \ x>0 \end{cases},](https://books.ung.si/app/uploads/quicklatex/quicklatex.com-9c8aad4f6de27622b1c90c49ba9a3b5e_l3.png) zvezna na
zvezna na ![]() .
.
![]()
Naloga 18: Izračunajte odvod funkcije ![]() , podane s predpisom.
, podane s predpisom.
Naloga 19: Po l’Hôpitalovem pravilu izračunajte naslednje limite:
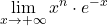
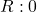
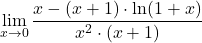
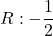
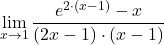
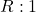
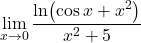
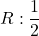
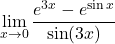
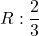
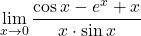
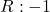 .
.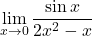
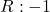
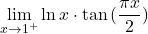 .
. 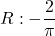
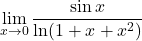
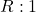
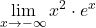
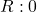
Naloga 20: Narišite graf funkcije ![]() , podane z naslednjimi predpisi:
, podane z naslednjimi predpisi: